Estimating your sweat rate can be a useful exercise when you’re trying to figure out how much and what you need to drink during training and events.
Sweat rate varies considerably from person-to-person due to body shape, size and fitness level. Your own sweat rate can also vary quite a lot as a multitude of factors - including how hard you’re working, the ambient temperature and humidity, wind speed, your clothing and heat acclimation status - all play a role in determining how fast and how much your body perspires.
Ideally, sweat rate measurement should be done on several occasions and in a range of conditions. So, you can then extrapolate the results and use them as a guide to dial in your fluid and electrolyte intake for an upcoming race...
How to calculate your sweat rate
Equipment needed:
- An accurate set of weighing scales
- A dry towel
- An accurate set of food scales to weigh your fuel and hydration (if you’re planning to eat and drink during the sessions where you’re measuring your sweat rate). Using the metric system (g, kg, ml, L) works best for this as 1 g = 1 ml.
Method:
This is slightly adapted from Asker Jeukendrup’s excellent mysportscience...
- Go for a pee and then record your body weight twice, after stepping on and off the scale, ideally with no clothes on. That’s A.
(If you can't weigh yourself in the buff because getting naked in public places like the local gym isn't your thing, you can always weigh your clothes and account for that weight difference - this is a method we call 'The Hovda Method').
2. Perform your session (or event) and record exactly how much you ate and drank.
This is easy if you drink from a single bottle or two.
Weigh your bottles before (That’s X) and after (Y) and record the difference. 1 gram = 1 millilitre.* (Z)
* If you use different measurement units, e.g. fl oz, you’ll need to convert all values to litres (via Google!). Make sure all units are in kg or litres
- After exercise, towel yourself dry and then record your weight, twice, again after stepping on and off the scale. Repeat this while clothed or nude (depending on which you did at the start. Nude is best as your clothes will hold some sweat). That’s B.
- Now subtract your post-exercise weight (B) from your pre-exercise weight (A) to get the weight you lost during the session.
Weight lost (C) = A-B
- Also subtract the weight of any fuel and hydration by weighing your bottle(s) and food before (X) and after (Y) to obtain the amount you consumed (Z).
Weight of fuel and hydration consumed (Z) = X-Y
6. You can now calculate your sweat rate…
(C+Z) / your exercise duration (in minutes)/60 minutes.
Note: It’s best not to use the bathroom at all during these sessions as this can skew the results. If you do have to go, in an ideal world you’d weigh yourself before and after to measure urine output, although a decent estimate is to assume a fluid loss of ~0.3L (300ml / 12oz) per bathroom stop.
You then just need to subtract 300ml (0.3kg) from your estimated sweat rate at the end.
I’d generally recommend trying to limit data collection to sessions lasting at least 60 minutes to 2 hours long. This is because anything shorter than that can be prone to errors of multiplication in the equations and doesn’t account for the time it takes to reach steady state sweating and may underestimate fluid losses over longer durations. Anything longer can start to be skewed by other non-sweat related sources of body mass change, including fuel utilisation (you inevitably burn glycogen during exercise and this can affect your body weight results), and respiratory water losses (a function of the amount of air moved in and out of your lungs as you breathe).
To make the above calculations really easy, you can collect all of the data into this spreadsheet along with some relevant notes about your session (mode of exercise, duration in minutes, rough intensity, temperature, whether it was outside or inside etc).
The sheet will then spit out a % bodyweight loss figure for that workout and also an estimate of your sweat rate expressed in litres per hour. Like this:
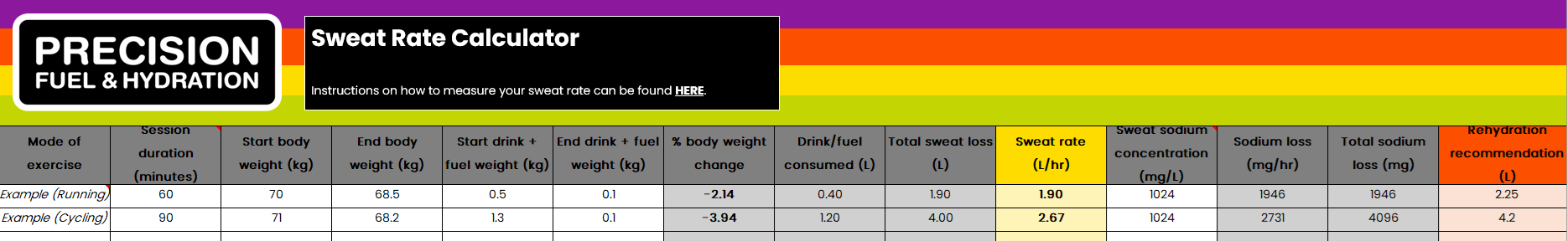
You can record numerous sessions in the sheet and this will help you to get a handle on what kind of range of sweat losses you see for different sports, in different weather conditions and at different intensities.
Though these calculations likely won’t be 100% accurate, they give you a good estimate of your sweat losses and will help categorise how sweaty you are. If you do this enough, you’ll become very good at ‘guesstimating’ your sweat rate in the future; a dinner party trick of dubious value if nothing else!
Plus, if you’ve also had a Sweat Test with us, you can add your sweat sodium concentration data in and it will estimate your hourly and total sodium loss numbers too, helping you get a good idea of what you’re losing so you can more adequately replace it.
Do you have a low, moderate or high sweat rate?
We often get asked what constitutes a low, moderate or high sweat rate by athletes taking our Fuel & Hydration Planner and it’s a tricky question to answer as there are a lot of variables involved.
A recent paper helpfully looked at a range of sweat rate data collected in a variety of sports and the graphs below show something of the trend in the data from 102 athletes in 340 trials:
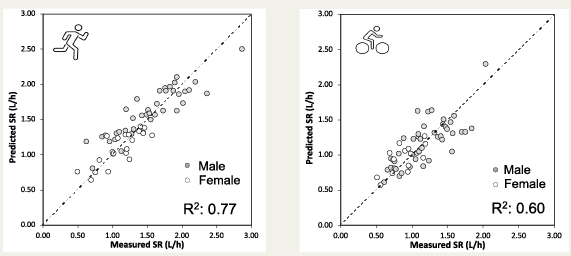
The range of sweat rates in the data was about 0.4 litres per hour to close to 3L/h (we have also observed as high as 3L/h in the Precision Performance Lab.
Another study done at the 2003 Hawaii Ironman in Kona came up with a very similar range of sweat rate figures in athletes a few days before the race.
Depending on your body shape and size (individuals with smaller body weights will typically sweat less than larger individuals as smaller people have lower absolute rates of heat production, which requires less sweat to keep you cool), anywhere from 0.5-1.5L/h are low-to-moderate sweat rates. These are common and relatively easy to manage from a fluid loss and hydration standpoint.
Anything much less than 0.5L/h would be on the low side for race intensities in mild conditions. Anything above 2.5L/h means you will start to run into issues with taking on enough fluids to remain hydrated during prolonged exercise in warm conditions.
Whilst we’ve seen those very high sweat rates of upwards of 3L/h in a handful of athletes, it tends to be in very, very big guys (men do tend to have higher sweat rates than women as men tend to have more muscle mass and therefore higher rates of metabolic heat production), and/or those working incredibly hard in oppressively hot and humid conditions.
Do bear in mind that body weight and size factor into all this, so if you’re a small female distance runner but you’re sweating at 1.5L/h, that might be considered a high or even very high sweat rate for you. On the flip side, the same number might be deemed quite low for a 6ft 11in (210cm), 150kg (330 lbs) Offensive Lineman in the NFL. But, I’m sure you get the general idea.
What to do with your sweat rate data
Once you’ve collected a reasonable amount of sweat rate data, the obvious question is "what can you do with the numbers?" And unfortunately the answer is not as straightforward as many athletes would like it to be.
Often you’ll see athletes performing these kinds of sweat rate tests and then proceeding to work out that an example sweat rate of 1L/h when running hard means they obviously need to drink 1L/h when running (i.e. to replace 100% of their losses).
There’s a nice simplicity to the concept of ‘1 out = 1 in’ and for a long time it was assumed that 100% sweat loss replacement during exercise was likely to deliver an optimal performance.
But time and research has shown that this logic is fundamentally flawed (the maintenance of performance in an exercising body is way to complex) and few, if any, credible sports scientists or nutritionists would advocate ‘like for like’ replacement of sweat losses during activity these days.
In fact, as 100% replacement often requires drinking beyond the body’s natural thirst instincts, it can be very dangerous. It carries the risk of hyponatremia (low blood sodium levels resulting in some nasty symptoms) if taken too far and this alone is enough to strongly discourage 100% fluid replacement as something to shoot for.
Do you need to replace 100% of your losses?
You can actually tolerate quite a bit of dehydration (as defined by body weight loss) during training and competition - assuming you start well hydrated. The exact amount you need to replace throughout your race is dependent on a few factors. The percentage of your sweat losses you should replace increases as your event duration increases (for example, when stepping up from an IRONMAN 70.3® to a full distance IRONMAN®) and as environmental conditions get more challenging. We know that dehydration exacerbates the impact of heat on exercise performance. In other words, the hotter you get and the conditions are the more important hydration is for performance.
This blog on how much dehydration you can tolerate is well worth a read as it gives some pointers on how much sweat you can probably lose before your performance is compromised and should help get your head around how much fluid you might want to be replacing.
It’s not productive to try to use sweat rate data to try to create a pre-determined, inflexible strategy for fluid and electrolyte replacement.
Measuring your sweat rate should be about getting to a pretty decent ‘ballpark’ figure for how much sweat (and sodium if you know your sweat composition) you’ll likely lose over a period of time, at a certain intensity and in a particular set of environmental conditions.
The reason we can’t use sweat rates from training and testing for hydration plans without question in races is that sweat rates are dependent on multiple factors, such as your power output or running speed/grade, environmental conditions (ambient temperature, relative humidity, solar radiation and wind speed), and clothing.
And so, without keeping these factors exactly the same between testing/training and racing, you can’t be certain of your sweat rates in different combinations of those factors. If you do enough of this testing in and around the type of scenarios you encounter in training and competing, it can be very helpful in working out the approximate levels of fluid and sodium intake that you’ll then go on to experiment with to optimise your performance.
It's worth noting that calculating sweat rate should be used as a GUIDE, and you should always defer to your body's signals in the moment to make adjustments. It's unrealistic to strictly follow a plan all the time because racing is dynamic (with fluctuations in speed, race temperatures, and physical conditions affecting metabolic rate and sweating rate/fluid loss in real time).
If you need some help with putting a hydration plan together to test in training, take our free Fuel & Hydration Planner. If you do that after getting some sweat rate data you’ll be able to answer our question on sweat rate with more confidence/accuracy.
Why sodium matters too...
Let’s say you’re losing ~0.5L of sweat per hour. It’s unlikely that you’re going to benefit from doing much more than drinking to thirst as, even over several hours, your total fluid and sodium losses are unlikely to get especially high.
But, if you’re losing more than 1.5L per hour then, during prolonged exercise, you’re likely to benefit from getting in front of the dehydration/sodium depletion curve with a pretty aggressive approach to hydration.
Taking proactive action during the early stages of big sessions and long events will help mitigate your inevitably high losses over the long haul. That’s especially the case if you also have a high sweat sodium concentration.
By measuring your sweat rate (and sweat concentration) and using this as a guide with differing levels of intake, you’re much more likely to iterate your way to the kind of hydration plan that will serve you well when it matters most.
This is just one part of the hydration equation...

As I’ve alluded to a few times, when it comes to understanding how to hydrate properly, you need to consider two things:
1, How much you’re sweating (i.e. your sweat rate, which we’ve covered in this article)
- How much salt you’re losing in that sweat (i.e. your sweat sodium concentration)...
If you’d like help gauging how salty your sweat is, read this post on how to estimate how much sodium you’re losing in your sweat.
